Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Sexual reproduction in plants is the process by which plants produce new offspring through the fusion of male and female gametes. It is the most common form of reproduction in plants, and it is essential for the long-term survival of plant species.
There are two main types of sexual reproduction in plants: self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Self-pollination occurs when pollen from a male flower is transferred to the female stigma of the same flower. This is the simplest form of sexual reproduction, and it is common in many plant species, such as beans, peas, and tomatoes.
Cross-pollination occurs when pollen from a male flower is transferred to the female stigma of a different flower. This is the most common form of sexual reproduction in flowering plants, and it is essential for the genetic diversity of plant populations.
Cross-pollination can be achieved by a variety of means, including wind, insects, and birds. Wind-pollinated plants often have small, lightweight pollen grains that are easily dispersed by the wind. Insect-pollinated plants often have bright flowers and sweet nectar to attract pollinators. Bird-pollinated plants often have large, brightly colored flowers and produce large quantities of nectar.
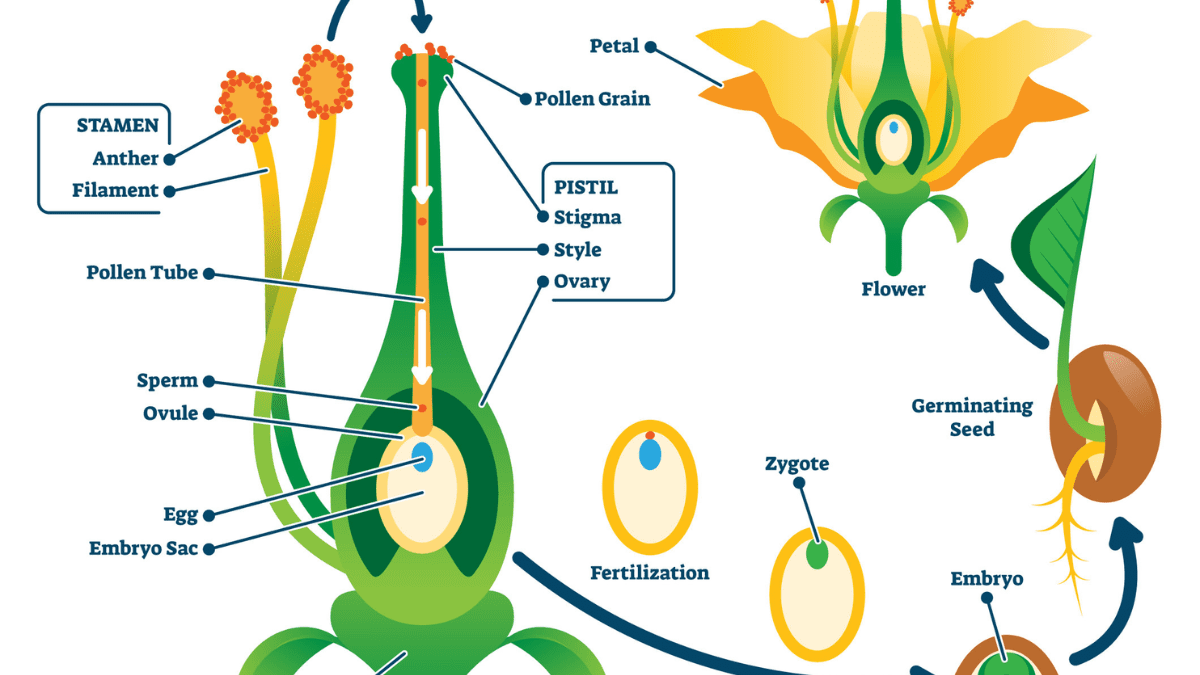
Once pollen has been transferred to the stigma of a flower, it germinates and produces a pollen tube. The pollen tube grows down the style of the flower and eventually reaches the ovary. In the ovary, the pollen tube releases the male gametes, which fuse with the female gametes to produce zygotes.
Zygotes are fertilized eggs, and they develop into seeds. Seeds contain an embryo, which is a young plant, and a food supply. Seeds are dispersed in a variety of ways, including by wind, water, and animals.
When a seed lands in a suitable location, it germinates and grows into a new plant.
The importance of sexual reproduction in plants
Sexual reproduction is important for plants for a number of reasons. First, it allows plants to produce new offspring that are genetically different from their parents. This genetic diversity is essential for the long-term survival of plant species.
Second, sexual reproduction allows plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions. For example, if a plant population is exposed to a new disease or pest, the genetic diversity of the population allows some individuals to survive and reproduce. These individuals can then pass on their resistance to the disease or pest to their offspring.
Finally, sexual reproduction allows plants to expand their range. When seeds are dispersed, they can land in new locations, where the plants can grow and reproduce. This allows plant populations to spread to new habitats and colonize new areas.
Conclusion
Sexual reproduction is an essential part of the life cycle of many plants. It allows plants to produce new offspring that are genetically different from their parents, which is important for the long-term survival of plant species. Sexual reproduction also allows plants to adapt to changing environmental conditions and to expand their range.
share
more_vert