
Sample Economics Question Paper-Hsc- Maharashtra Board
Subject: Economics
Standard: 12th
Total Marks: 80
Q.1. A) Choose the correct option 5 Marks
1) Concepts studied under microeconomics.
a) National Income b) General price level
c) Factor Pricing d) Product Pricing.
Options: 1) b and c 2) b, c and d 3) a, b and c 4) c and d
2) Homogeneous product is the feature of this market:
a) Monopoly b) Monopolistic Competition
c) Perfect Competition d) Oligopoly.
Options: 1) c and d 2) a, b and c 3) a, c and d 4) only c
3) The transfer income is:
a) Revenue received by selling goods. b) Payment received by labour.
c) Profit earned from business. d) Pension.
Option: 1) only d 2) only b 3) b and c 4) b and d
4) Types of foreign Trade:
a) Import Trade b) Export Trade
c) Entrepot Trade d) internal Trade
Options : 1) a and b 2) c and d 3) a, b and c 4) None of these
5) In India, National Income is estimated using:
a) Output Method b) Income Method
c) Expenditure Method d) Combination of input and output method
Option: 1) only b 2) only c 3) a and c 4) only d
B) Complete the correlation. 5 Marks
1. Micro Economics : Slicing Method : : Macro Economics:_________.
2. Capital : Derived Demand : : Umbrella :________.
3. Capital : Interest : : Entrepreneur :_________.
4. Money Market : Short term funds : : _______: Long term funds
5. Demand curve: ________ :: Supply curve : Upward.
C) Assertion and reasoning. 5 Marks
1. Assertion (A) : Microeconomics has comparatively narrower scope.
Reasoning (R) : Microeconomics studies economic behaviour of only individual economic unit of economy.
Options: 1) (A) is true, but (R ) is false.
2) (A) is false, but (R ) is true.
3) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is the correct explanation of (A).
4) ) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is not the correct explanation of (A)
2. Assertion (A) :Elasticity of demand explains that one variable is influenced by another variable.
Reasoning (R) : The concept of elasticity of demand indicates the effect of price and changes in other factor of demand.
Options: 1) (A) is true, but (R ) is false.
2) (A) is false, but (R ) is true.
3) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is the correct explanation of (A).
4) ) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is not the correct explanation of (A).
3. Assertion (A) : Demand for furniture is relatively elastic.
Reasoning (R) : The consumption of furniture can be postponed.
Options: 1) (A) is true, but (R ) is false.
2) (A) is false, but (R ) is true.
3) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is the correct explanation of (A).
4) ) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is not the correct explanation of (A).
4. Assertion (A) : In monopoly, use wise price can be discriminated.
Reasoning (R) : In India, the gas cylinder is priced the same for domestic and commercial use.
Options: 1) (A) is true, but (R ) is false.
2) (A) is false, but (R ) is true.
3) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is the correct explanation of (A).
4) ) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is not the correct explanation of (A).
5. Assertion (A) : Government sells bonds to its citizens.
Reasoning (R) : Selling bond is important type of internal debt.
Options: 1) (A) is true, but (R ) is false.
2) (A) is false, but (R ) is true.
3) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is the correct explanation of (A).
4) ) Both (A) and (R ) are true and (R ) is not the correct explanation of (A).
D) Find the odd word out 5 Marks
1. Air, Water, Sunlight, Gold.
2. Washing Machine, Wooden chair, Cupboard, Milk.
3. Selling cost: Free gifts, Advertisement hoardings, window display, patents.
4. Price index number, Quantity index number, paasche’s index number, Value index number.
5. Fees, Gifts, Grants, Goods and Services Tax.
Q. 2. A) Identify and explain the concepts (Any 3) 6 Marks
1. Rajesh decided to count how many times he had to travel by rickshaw in a period of one month.
2. Although gold is not necessary for survival, the price of gold is high.
3. Viru kept aside 100 kg out of 500 kg of wheat produced in his farm for his family.
4. Tina deposited a lump sum amount of Rs. 50,000 in the bank for a period of one year.
5. India purchased petroleum from Iran.
B) Distinguish between (Any 3) 6 Marks
1. Total utility and Marginal Utility.
2. Perfect competition and Monopoly.
3. Direct Tax and Indirect Tax.
4. Gross Domestic Product and Gross National Product.
5. Demand Deposits and Time Deposits.
Q. 3) Answer in brief (Any 3) 12 Marks
1. Explain the importance of Foreign Trade.
2. Explain the types of utility.
3. Explain the features of Index number.
4. Explain non-tax sources of revenue of the government.
5. Explain the concept of Total Cost and Total Revenue.
Q.4) State with reasons whether you agree or disagree. (Any 3) 12 Marks
1. A seller is price maker in Monopoly.
2. Index number can be constructed without the base year.
3. Gross National product and Gross Domestic Product are same concepts.
4. Commercial banks accept various types of deposits.
5. Public finance is more elastic than private finance.
Q.5) Study the following table, figure, passage and answer the question given below. (Any 2) 8 Marks
1. Study the following table and answer the question:
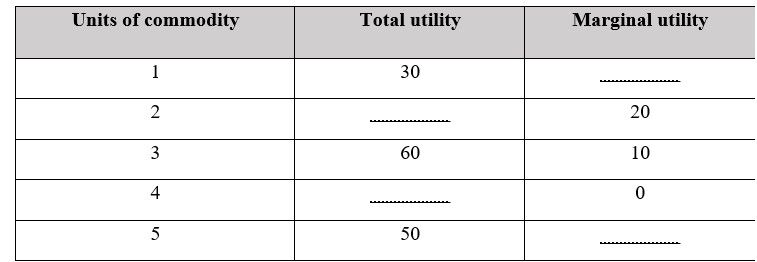
Questions:
1. Complete the table.
2. The consumers will derive the maximum satisfaction in the place of fourth unit. State, with reason, whether this statement is true or false.
2. Study the following diagram and answer the question given below:
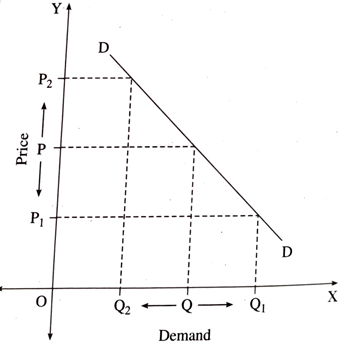
Questions:
1. When the price of the commodity is OP, the demand of the commodity is .
2. QQ1 distance indicates in demand.
3. QQ2 distance indicates in demand.
4. The slope of the demand curve is .
3. Study the following passage and answer the questions given below it:
The conventional notion of social security is that the government would make periodic payments to look after people in their old age, ill-health, disability and poverty. This idea should itself change from writing a cheque for beneficiary to institutional arrangements to care for beneficiaries, including by enabling them to look after themselves, to a large extent.
The write-a-cheque model of social security is a legacy from the rich world at the optimal phase of its domestic transition, when the working population was numerals enough and earning enough to generate the taxes to pay for the care of those not working. This model is ill-suited for less, well-off India with growing life expectancy, increasing urbanization and resultant migration. Social security under urbanization will be different from social security in a static society.
Questions:
(1) State the conventional notion of social security.
(2) What kind of conceptual change is suggested in the given paragraph.
Q. 6) Answer in detail. (Any 2) 16 Marks
1. State the law of Demand. What are the assumptions to the law of Demand?
2. What is Monopolistic competition? Explain in detail the features of Monopolistic competition
3. Explain the difficulties in measuring the national income.
Appreciate the creator