
Post vs Put vs Patch - Http Methods
There is always a confusion between when to use PUT, PATCH or POST methods to create/update a resource. This article covers what are the difference between these methods.
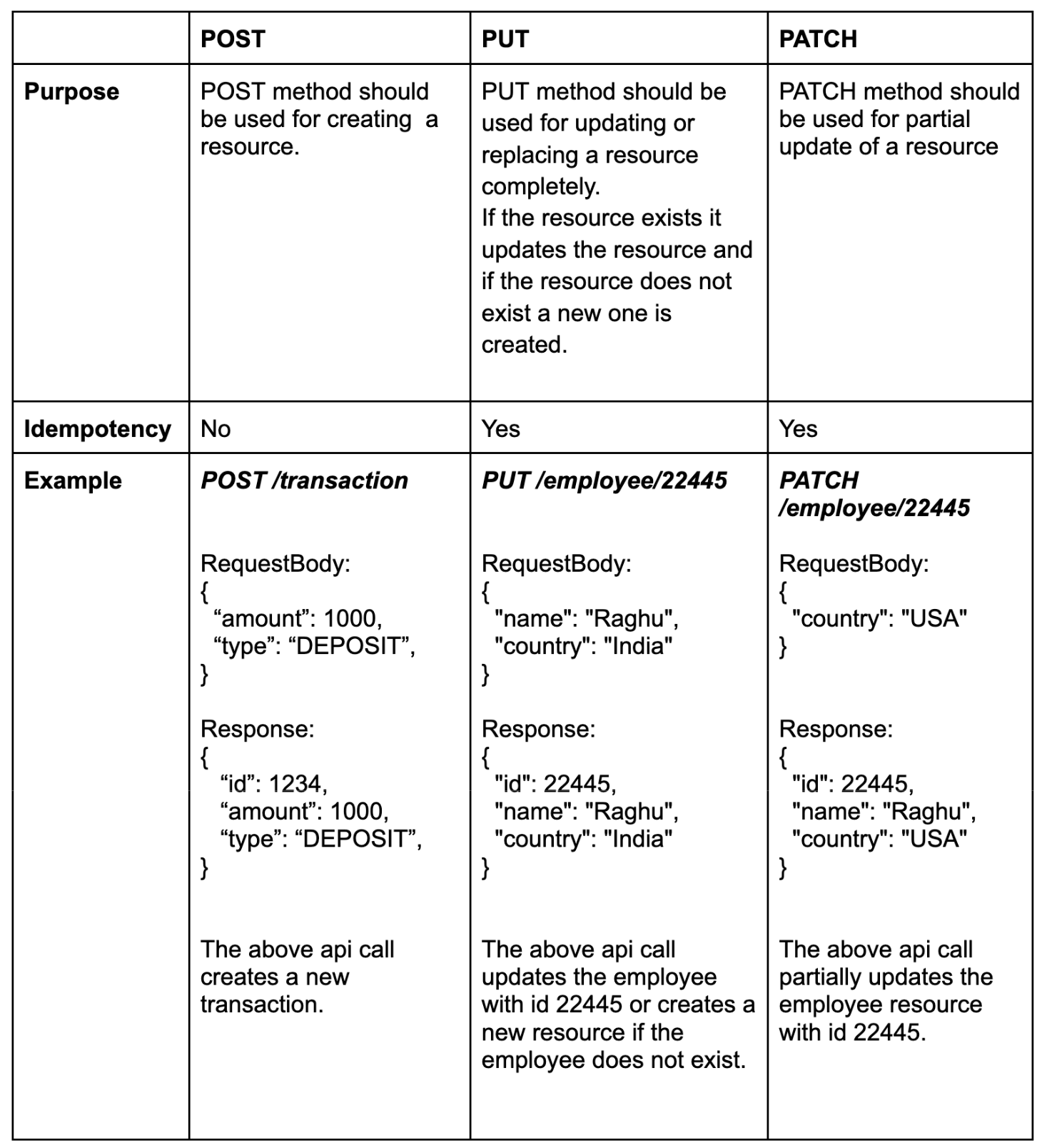
POST
It should be used for creating a new resource.
Example:
POST /transaction
RequestBody:
{
"amount": 100,
"type": "DEPOSIT"
}
Response:
{
"id": 1234,
"amount": 100,
"type": "DEPOSIT"
}The above api call creates a new transaction and returns the transaction resource with id in the response.
Idempotency: POST method is not idempotent. If you take the below example if the same request is made multiple times then total amount reflected in the bank account will be "200" as the system would have create two transaction resource.
Request1:
POST /transaction
RequestBody
{
"amount": 100,
"type": "DEPOSIT"
}
Request2:
POST /transaction
RequestBody
{
"amount": 100,
"type": "DEPOSIT"
} PUT
It is used for completely updating an existing resource or in other words replaces an existing resource. If resource does not exists it creates a new resource.
Example:
PUT /employee/22445
RequestBody:
{
"name": "Raghu",
"country": "India"
}
Response:
{
"id": 22445,
"name": "Raghu",
"country": "India"
}The above request updates/replaces the employee resource if the employee id (22445) already exists in the system if the employee id does not exist a new resource will be created.
Idempotency: PUT method is idempotent. If the below request is called multiple times, it would result in the same outcome, i.e the employee resource with id "2245" will be updated.
PATCH
It should be used for partial update of existing resource.
Example:
PATCH /employee/22445
RequestBody
{
"country": "USA"
}
Response:
{
"id": 22445,
"name": "Raghu",
"country": "USA"
}The above requests updates the country to "USA" for employee with id 22445.
Idempotency: PATCH method is idempotent. If the below request is called multiple times, it would result in the same outcome, i.e the employee resource with id "2245" will be updated.
Quick Summary
Appreciate the creator