
Html Introduction
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It is used to design web pages using a markup language. HTML is a combination of Hypertext and Markup language. Hypertext defines the link between web pages. A markup language is used to define the text document within the tag which defines the structure of web pages. This language is used to annotate (make notes for the computer) text so that a machine can understand it and manipulate text accordingly. Most markup languages (e.g. HTML) are human-readable. The language uses tags to define what manipulation has to be done on the text.
HTML is a markup language used by the browser to manipulate text, images, and other content, to display it in the required format. HTML was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1991. The first-ever version of HTML was HTML 1.0, but the first standard version was HTML 2.0, published in 1995.
Elements and Tags: HTML uses predefined tags and elements which tell the browser how to properly display the content. Remember to include closing tags. If omitted, the browser applies the effect of the opening tag until the end of the page.
HTML page structure: The basic structure of an HTML page is laid out below. It contains the essential building-block elements (i.e. doctype declaration, HTML, head, title, and body elements) upon which all web pages are created.
<!DOCTYPE html>: This is the document type declaration (not technically a tag). It declares a document as being an HTML document. The doctype declaration is not case-sensitive.
<html>: This is called the HTML root element. All other elements are contained within it.
<head>: The head tag contains the “behind the scenes” elements for a webpage. Elements within the head aren’t visible on the front end of a webpage. HTML elements used inside the <head> element include:
<style>-This HTML tag allows us to insert styling into our web pages and make them appealing to look at with the help of CSS.
<title>-The title is what is displayed on the top of your browser when you visit a website and contains the title of the webpage that you are viewing.
<base>-It specifies the base URL for all relative URLs in a document.
<noscript>– Defines a section of HTML that is inserted when the scripting has been turned off in the user's browser.
<script>-This tag is used to add functionality to the website with the help of JavaScript.
<meta>-This tag encloses the metadata of the website that must be loaded every time the website is visited. For eg:- the metadata charset allows you to use the standard UTF-8 encoding on your website. This in turn allows the users to view your webpage in the language of their choice. It is a self-closing tag.
<link>– The ‘link’ tag is used to tie together HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It is self-closing.
<body>: The body tag is used to enclose all the visible content of a webpage. In other words, the body content is what the browser will show on the front end.
An HTML document can be created using any text editor. Save the text file using .html or .htm. Once saved as an HTML document, the file can be opened as a webpage in the browser.
Note: Basic/built-in text editors are Notepad (Windows) and TextEdit (Macs). Basic text editors are entirely sufficient for when you’re just getting started. As you progress, there are many feature-rich text editors available which allow for greater function and flexibility.
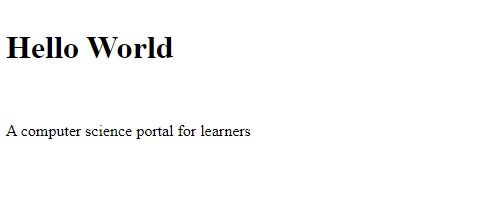
Example: This example illustrates the basic structure of HTML code.
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo Web Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<p>A computer science portal for learners </p>
</body>
</html>Output:
Features of HTML:
It is easy to learn and easy to use.
It is platform-independent.
Images, videos, and audio can be added to a web page.
Hypertext can be added to the text.
It is a markup language.
Why learn HTML?
It is a simple markup language. Its implementation is easy.
It is used to create a website.
Helps in developing fundamentals about web programming.
Boost professional career.
Advantages:
HTML is used to build websites.
It is supported by all browsers.
It can be integrated with other languages like CSS, JavaScript, etc.
Disadvantages:
HTML can only create static web pages. For dynamic web pages, other languages have to be used.
A large amount of code has to be written to create a simple web page.
The security feature is not good.
HTML is the foundation of web pages and is used for webpage development by structuring websites and web apps. You can learn HTML from the ground up by following this HTML Tutorial and HTML Examples.
Appreciate the creator