
From 3d to 4d Printing: Advancements, Advantages, & Opportunities
What is 4D Printing technology and its future scope?
4D printing is an emerging technology that builds on the concept of 3D printing, adding a fourth dimension of time. In 4D printing, materials are designed to change shape or function over time in response to certain stimuli such as heat, light, moisture, or pressure. This is made possible by printing objects with smart materials that have the ability to self-assemble, self-repair, or change their physical properties over time.
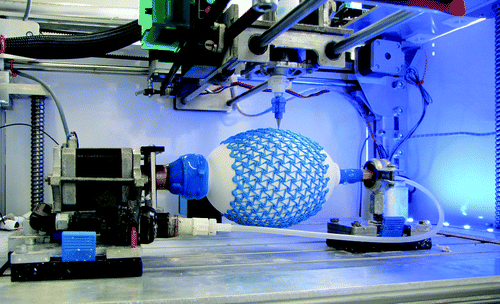
The future scope of 4D printing is vast and holds tremendous potential in various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and construction. Here are some possible applications of 4D printing:
Self-assembling furniture and toys: 4D printing can enable the creation of objects that can self-assemble without the need for complex assembly instructions or tools.
Smart clothing: Smart fabrics can be designed to change shape or function based on changes in the environment, such as temperature, moisture, or pressure.
Biomedical devices: 4D printing can be used to create medical devices that can adapt to the changing needs of the human body, such as drug delivery systems, stents, and prosthetics.
Construction materials: 4D printed materials can be designed to adapt to changing environmental conditions, such as earthquakes, by changing their shape or stiffness.
According to FactMR, a market research and competitive intelligence provider, the United States 4D Printer market amounted to US$ 40 million.
The global 4D printing market is predicted to increase at a stupendous CAGR of 35.4% and touch a valuation of US$ 2.5 billion by 2033.
Request PDF Sample of 4D Printing Market Report - Fact.MR
Comparison of 4D Printing with 3D Printing
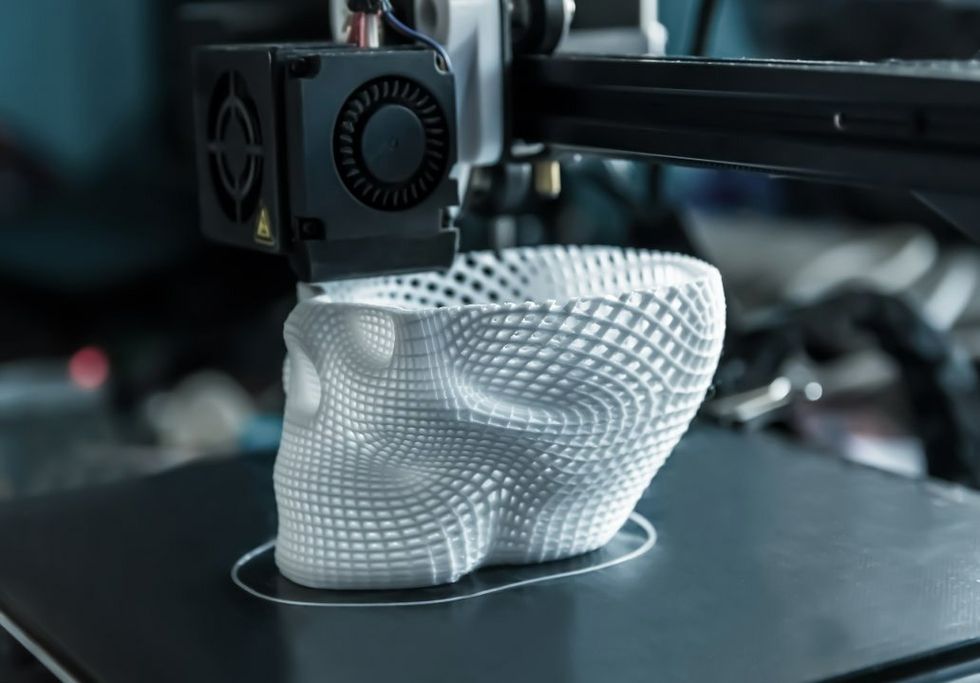

4D printing is an advanced form of 3D printing that adds an additional dimension of time. Here are some key differences between 3D printing and 4D printing:
Material properties: 3D printing uses a variety of materials such as plastics, metals, and ceramics, while 4D printing uses smart materials that can change their properties over time in response to external stimuli.
Object structure: In 3D printing, objects are typically built layer by layer using a fixed design, whereas 4D printed objects can self-assemble, self-repair, or change their shape or function over time.
Design complexity: 4D printing allows for more complex designs than 3D printing because it enables the creation of objects with multiple parts that can move independently, allowing for more intricate shapes and functions.
Stimuli: 4D printing requires the use of stimuli such as heat, light, or moisture to trigger the transformation of the smart materials, whereas 3D printing does not require any external stimuli.
Applications: 3D printing is commonly used in prototyping and small-scale production, while 4D printing is still in its early stages of development and has the potential to be used in a variety of industries, such as construction, healthcare, and aerospace.
Benefits of 4D Printing
4D printing has several potential benefits over traditional manufacturing methods. Here are some of the key benefits of 4D printing:
Customization: 4D printing allows for the creation of objects with customized shapes and functions that can adapt to different environments or use cases.
Complexity: 4D printing enables the creation of more complex and intricate designs than traditional manufacturing methods.
Self-assembly: 4D printed objects can self-assemble, reducing the need for manual assembly and reducing the risk of errors.
Reduced waste: 4D printing can reduce waste by creating objects with the precise amount of material needed and by enabling the creation of objects with multiple functions in a single print.
Reduced cost: 4D printing can reduce manufacturing costs by simplifying assembly processes and reducing the need for specialized tools.
Sectors that could benefit from 4D printing include:
Healthcare: 4D printing can be used to create medical devices and implants that can adapt to the changing needs of the human body.
Construction: 4D printing can enable the creation of building materials that can adapt to changing environmental conditions, reducing the risk of damage from natural disasters.
Aerospace: 4D printing can be used to create lightweight, complex, and adaptive components for aircraft and spacecraft.
Manufacturing: 4D printing can simplify the assembly process and reduce waste, making it a cost-effective manufacturing method for small-batch or custom products.
Robotics: 4D printing can be used to create self-assembling robots that can adapt to different environments and perform multiple functions.
Overall, 4D printing has the potential to revolutionize manufacturing and design in a variety of industries, creating more efficient and adaptive products that better meet the needs of consumers and businesses.
Request PDF Sample of 4D Printing Market Report - Fact.MR
Appreciate the creator