Electric Potential and Potential Difference
Electric Potential and Potential Difference
simple circuit with a battery, a resistor, and a light bulb
Electric Potential
Electric potential, also known as electric voltage or simply voltage, is a measure of the potential energy per unit charge of an electric field. It is defined as the work done per unit charge to move a small charge from infinity to a given point in the electric field. The SI unit of electric potential is the volt (V).
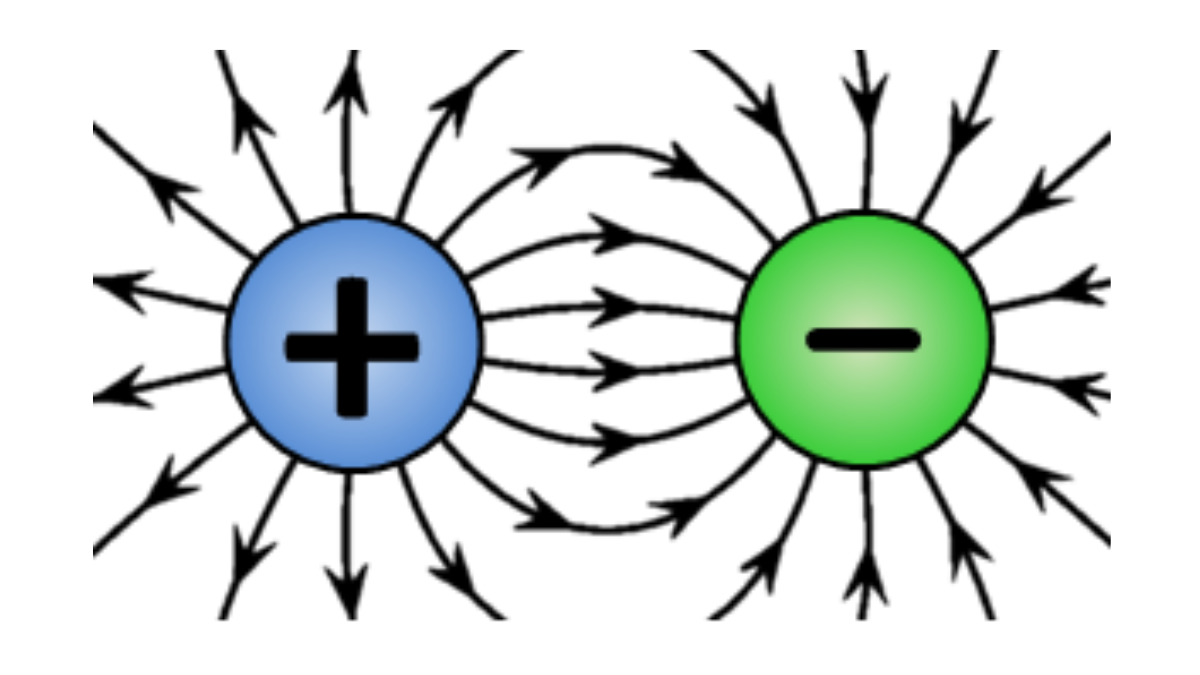
Image of electric potential diagram
In other words, electric potential is the amount of work that must be done to move a small charge from infinity to a given point in an electric field. The amount of work required depends on the strength of the electric field and the distance that the charge is moved.
Electric potential is a scalar quantity, meaning that it has no direction. It is also a relative quantity, meaning that it is always measured relative to a reference point. The reference point is typically chosen to be infinity.
Potential Difference
electric potential difference diagram
Potential difference, also known as voltage difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points in an electric field. It is defined as the work done per unit charge to move a small charge from one point to another. The SI unit of potential difference is also the volt (V).
In other words, potential difference is the amount of work that must be done to move a small charge from one point to another in an electric field. The amount of work required depends on the difference in electric potential between the two points.
Potential difference is a scalar quantity, meaning that it has no direction. It is also a relative quantity, meaning that it is always measured between two points.
Relationship Between Electric Potential and Potential Difference
Electric potential and potential difference are related to each other by the following equation:
ΔV = V₂ - V₁
where:
ΔV is the potential difference between two points
V₂ is the electric potential at the second point
V₁ is the electric potential at the first point
The equation states that the potential difference between two points is equal to the difference in electric potential between the two points.
Applications of Electric Potential and Potential Difference
Electric potential and potential difference are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
Electronics: Electric potential and potential difference are used to power electronic devices, such as transistors and diodes.
Batteries: Batteries store electrical energy in the form of chemical energy. The potential difference between the terminals of a battery is a measure of the amount of electrical energy that the battery can store.
Electric motors: Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The potential difference between the terminals of an electric motor is a measure of the amount of torque that the motor can produce.
Transmission lines: Transmission lines are used to transport electrical energy from power plants to consumers. The potential difference between the wires in a transmission line is a measure of the amount of electrical energy that can be transported.
Conclusion
Electric potential and potential difference are important concepts in physics and engineering. They are used to describe the behavior of electric fields and to design electrical circuits.