
Electric Flux
Electric flux, a fundamental concept in electromagnetism, represents the amount of electric field passing through a surface. This quantitative measure provides valuable insights into the behavior of electric fields and their interactions with matter.
Electric flux
Unveiling the Essence of Electric Flux
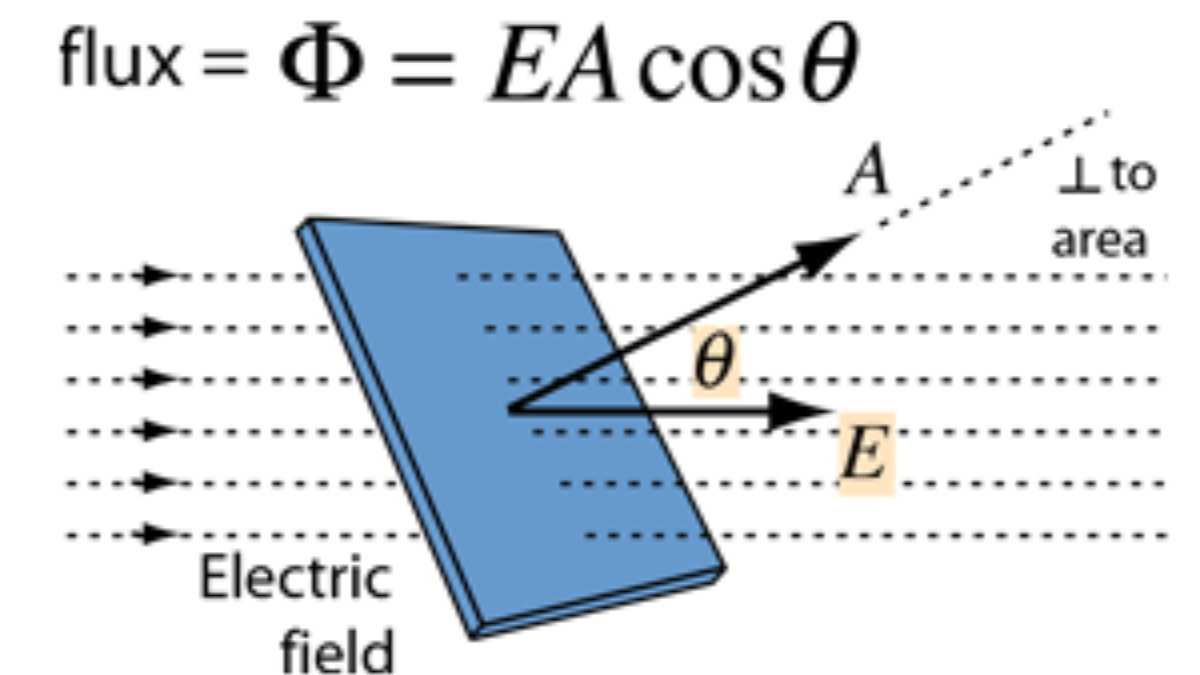
Electric flux (Φ) is defined as the product of the electric field (E) and the area (A) of the surface through which it passes:
Φ = E * A * cos(theta)
where theta is the angle between the electric field and the normal vector to the surface.
The SI unit of electric flux is the newton meter squared per coulomb (N·m^2/C).
Interpreting Electric Flux
The value of electric flux can be interpreted in two ways:
Total Electric Field Crossing the Surface: Electric flux represents the total amount of electric field passing through a surface, providing a quantitative measure of the electric field's strength and direction.
Number of Electric Field Lines Passing the Surface: Electric flux can be visualized as the number of electric field lines passing through a surface. Each electric field line represents a path of an electric charge, and their density indicates the strength of the electric field.
Properties of Electric Flux
Electric flux exhibits several notable properties:
Sign Convention: The sign of electric flux depends on the angle between the electric field and the normal vector to the surface. If the electric field is aligned with the normal vector, the flux is positive. If the electric field is opposed to the normal vector, the flux is negative.
Flux Through a Closed Surface: The total electric flux through a closed surface is zero. This implies that electric field lines always start and end at charges, forming continuous loops.
Gauss's Law: Electric flux is mathematically related to the charge enclosed by a surface through Gauss's law, a fundamental principle in electromagnetism.
Applications of Electric Flux
Electric flux has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
Charge Distribution Analysis: Electric flux can be used to determine the charge distribution within a region by analyzing the flux through a closed surface enclosing the region.
Electric Field Calculation: Electric flux can be used to calculate the average electric field over a surface.
Electromagnetic Wave Propagation: Electric flux plays a crucial role in understanding the propagation of electromagnetic waves, including light and radio waves.
Material Science: Electric flux is used to analyze the polarization of materials, where electric dipoles are aligned, influencing their dielectric properties.
Electric Device Design: Electric flux is considered in the design of various electric devices, such as capacitors and particle accelerators.
Conclusion: Electric Flux – A Fundamental Measure in Electromagnetism
Electric flux, with its profound implications and diverse applications, stands as a cornerstone of electromagnetism. Its understanding is essential for comprehending the behavior of electric fields and their interactions with matter. From charge distribution analysis to electromagnetic wave propagation, electric flux serves as a powerful tool in unraveling the mysteries of electromagnetism and shaping technological advancements.
Appreciate the creator