
Charle's Law
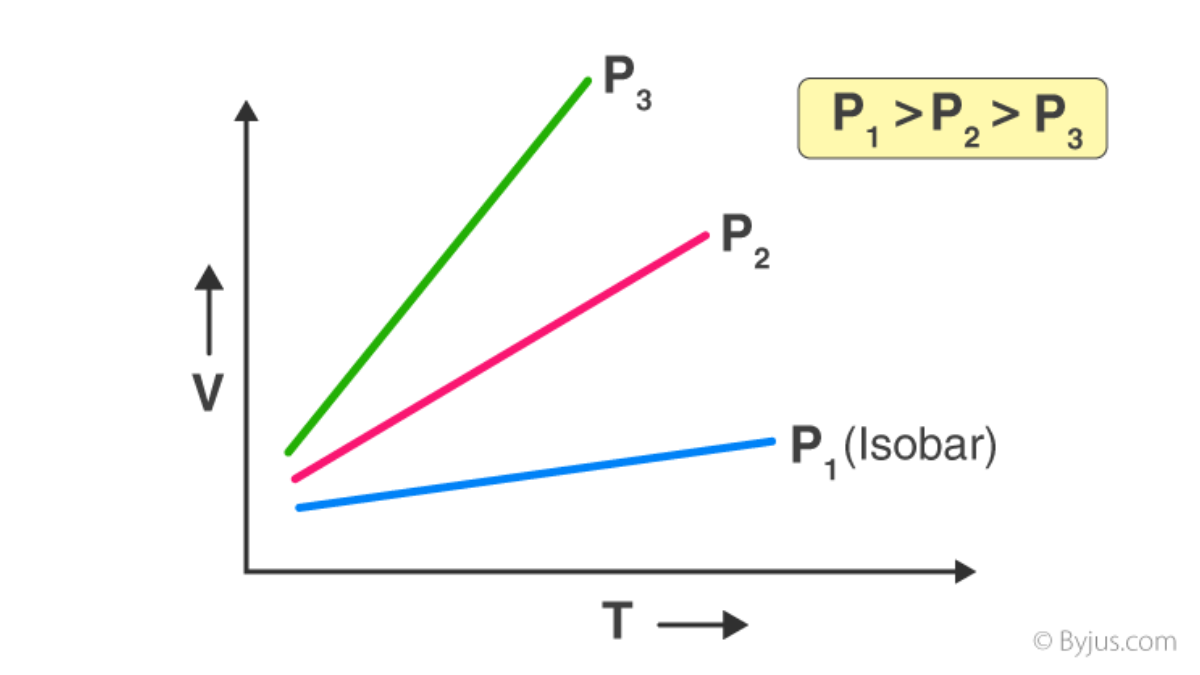
Charle's law, also known as the law of volumes, is one of the gas laws that describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas at a constant pressure. It states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature, provided that the pressure and the amount of gas remain constant.
Mathematically, Charle's law can be expressed as follows:
V/T = k
where:
V is the volume of the gas
T is the temperature of the gas
k is a constant
This means that as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, and vice versa.
Charle's law can be used to explain a variety of phenomena, such as the hot air balloon and the air conditioning system. In a hot air balloon, the air inside the balloon is heated, which causes it to expand and lift the balloon off the ground. In an air conditioning system, the refrigerant gas is compressed and then expanded, which causes it to cool and absorb heat from the surrounding air.
Here are some examples of Charle's law in action:
When you blow up a balloon and then put it in the freezer, the balloon will shrink. This is because the temperature of the air inside the balloon has decreased, causing the volume to decrease.
When you open a can of soda on a hot day, the soda fizzes out. This is because the temperature of the soda has increased, causing the volume to increase.
When you use a hair dryer, the air coming out of the dryer is hot. This is because the hair dryer compresses and then expands the air, which causes it to heat up.
Charle's law is an important law of physics that has many applications in the real world. It is used by scientists and engineers to design and operate a variety of devices, such as hot air balloons, air conditioning systems, and hair dryers.
Applications of Charle's Law
Charle's law has a number of applications in everyday life and in industry. Here are a few examples:
Hot air balloons: The air inside a hot air balloon is heated, which causes it to expand and lift the balloon off the ground.
Air conditioning: The refrigerant gas in an air conditioning system is compressed and then expanded, which causes it to cool and absorb heat from the surrounding air.
Hair dryers: The air coming out of a hair dryer is hot because the hair dryer compresses and then expands the air, which causes it to heat up.
Respiratory therapy: Charle's law is used to design and operate ventilators, which are machines that help people breathe.
Food processing: Charle's law is used to design and operate food processing equipment, such as freezers and dryers.
Chemical engineering: Charle's law is used to design and operate chemical processing equipment, such as reactors and distillers.
Charle's law is an important law of physics that has many applications in the real world. It is used by scientists and engineers to design and operate a variety of devices, from hot air balloons to air conditioning systems to chemical processing equipment.
Appreciate the creator